Event loop in JavaScript
Task of Rolling Scopes School
Created by BertFrontEnd
So, who tells the JS engine that he needs to execute some piece of the program?
A common characteristic of all such environments is a built-in mechanism called an Event Loop
Take a look at the following diagram
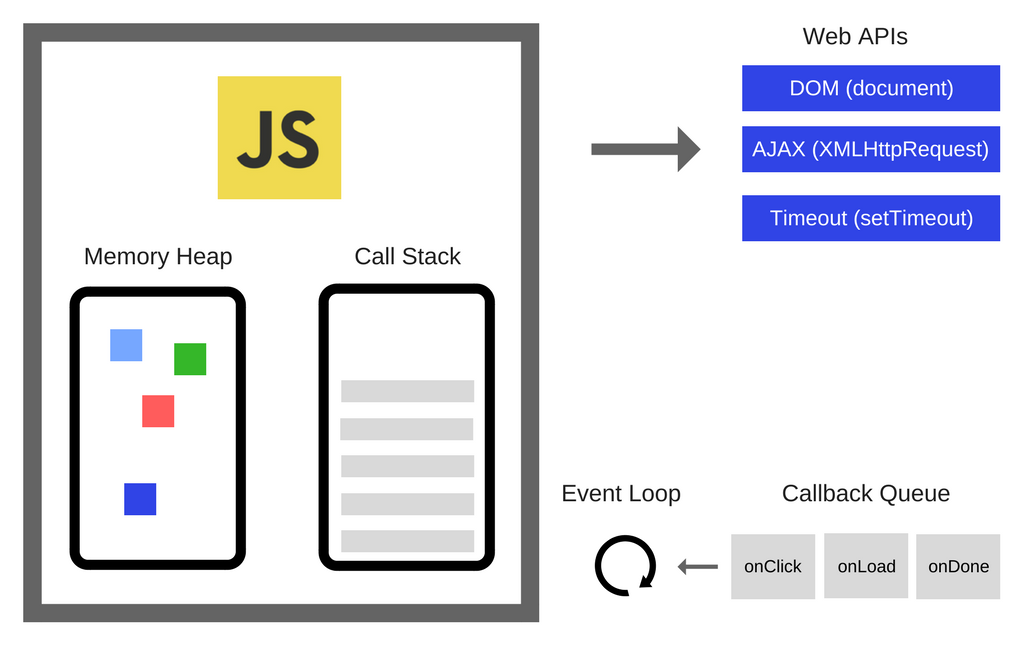
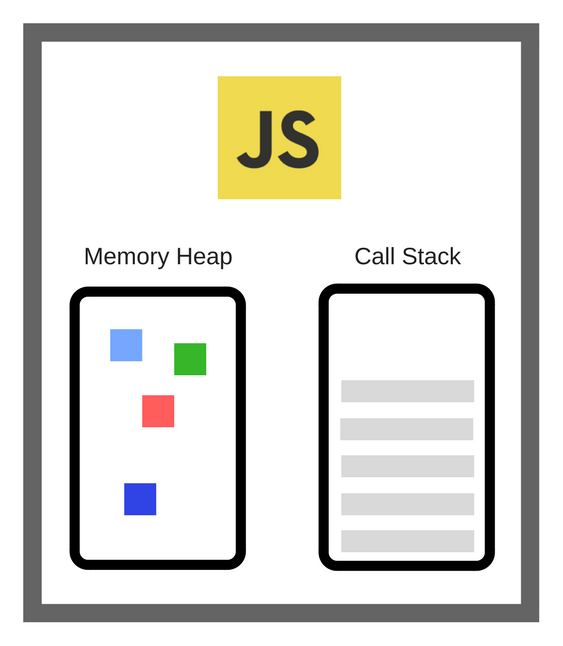
Here we see the JS-engine. It has two main components: Heap or Memory Heap and Call Stack
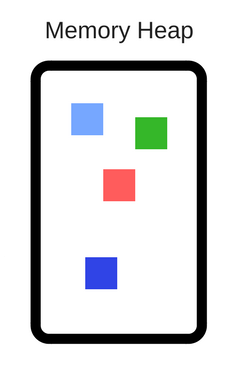
Heap or Memory Heap - is where memory allocation takes place

Call Stack - is where the so-called stack frames fall into the process of executing the code
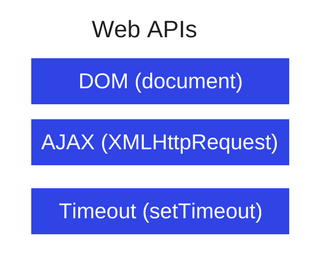
What are the Web APIs?
These are flows to which we do not have direct access, we can only perform calls to them. They are built into the browser, where asynchronous actions are performed
So, what is the Event Loop itself? Let's take a look at the following down
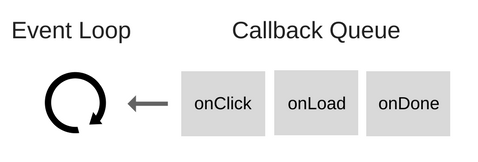
The Event Loop solves one main problem: it monitors the Call Stack and the Callback Queue
Consider the following example
console.log('Hi');
setTimeout(function cb1() {
console.log('cb1');
}, 5000);
console.log('Bye');
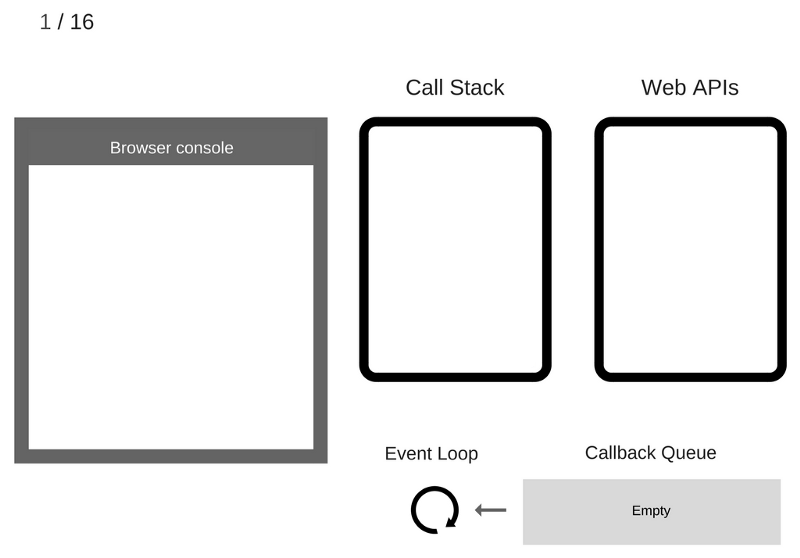
Let's take a step-by-step “execution” of this code and see what happens in the system
Nothing is happening yet - the browser console is clean, the Call Stack is empty
The console.log('Hi') command is added to the Call Stack
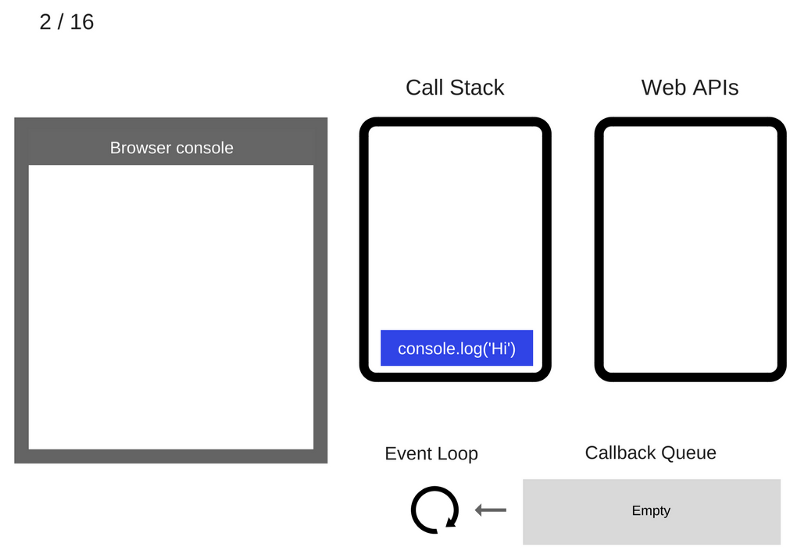
The console.log('Hi') command is executed
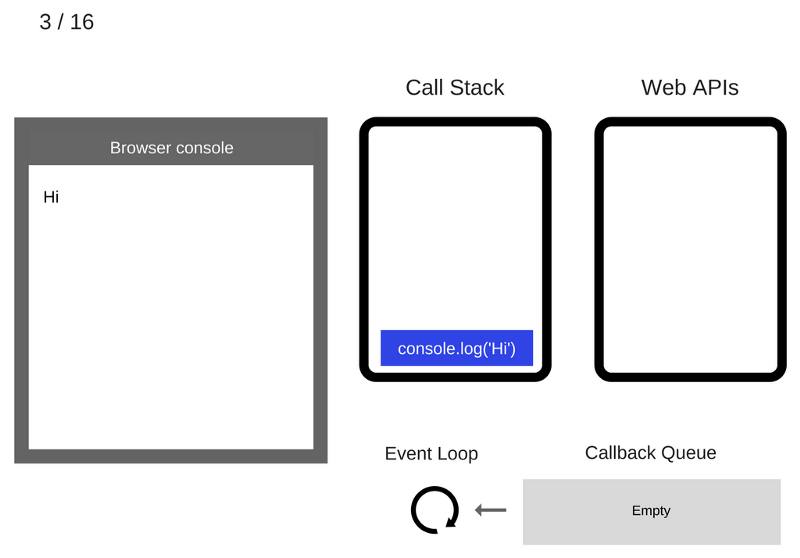
The console.log ('Hi') command is removed from the Call Stack
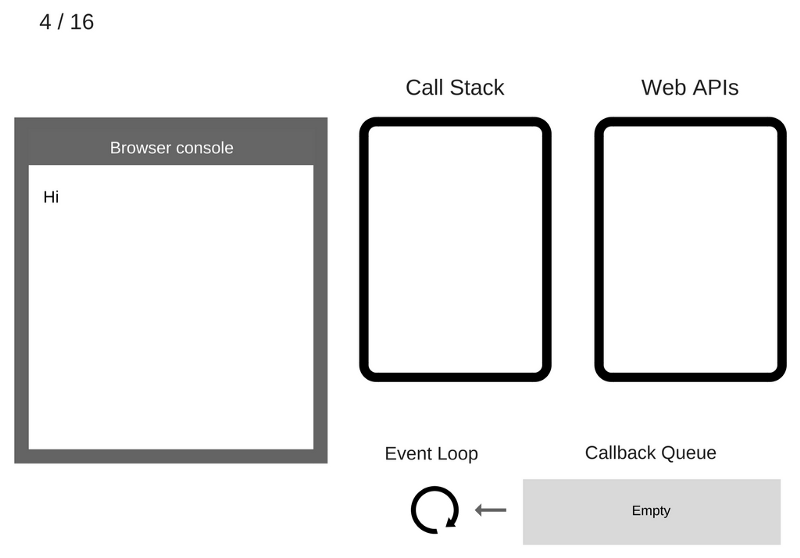
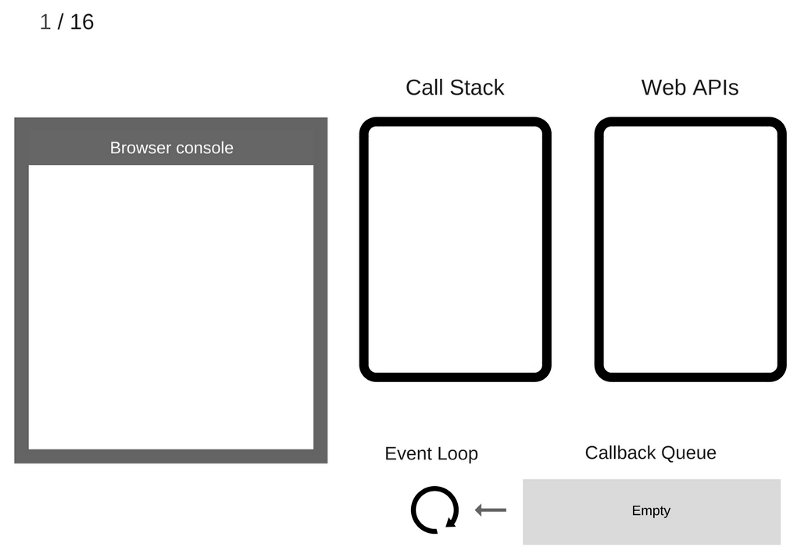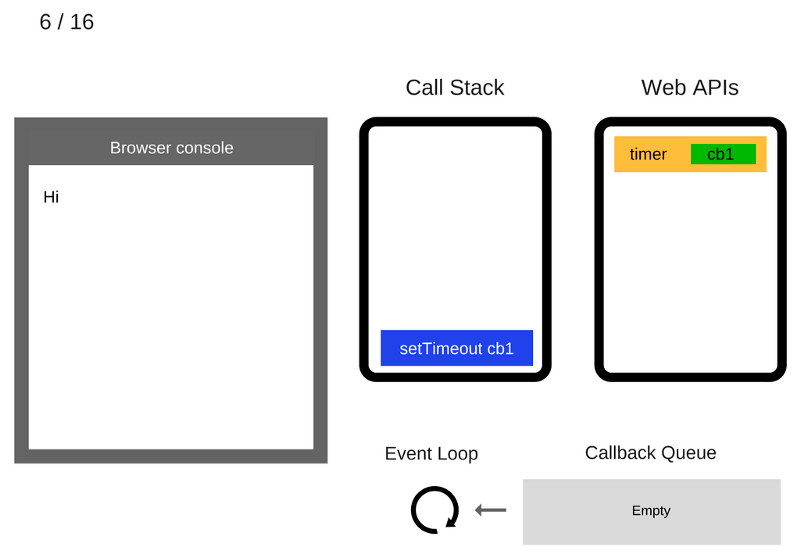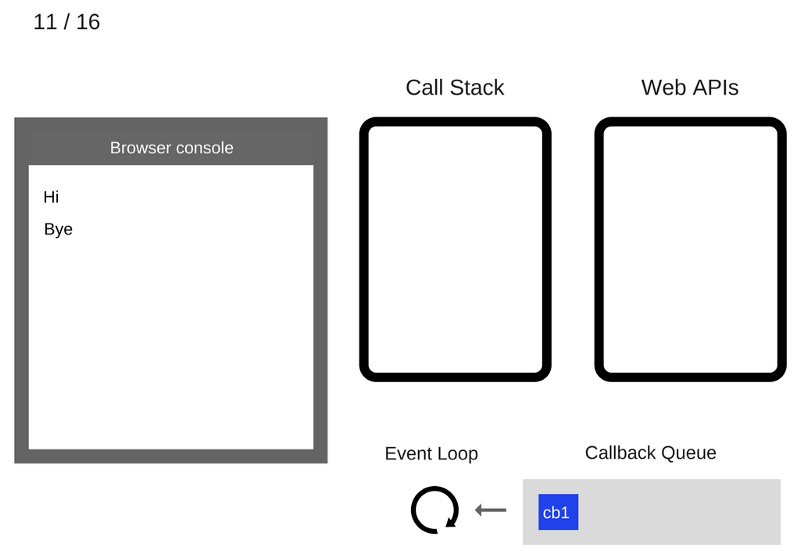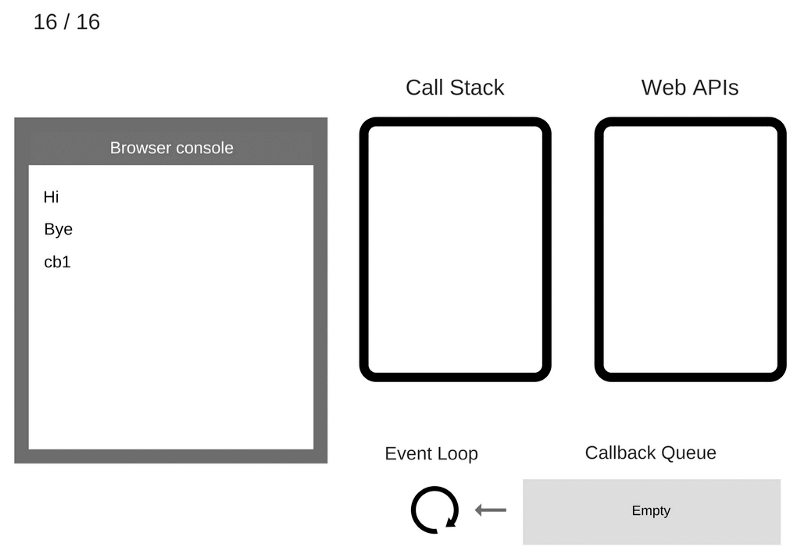
The setTimeout (function cb1 () {...}) command is added to the Call Stack
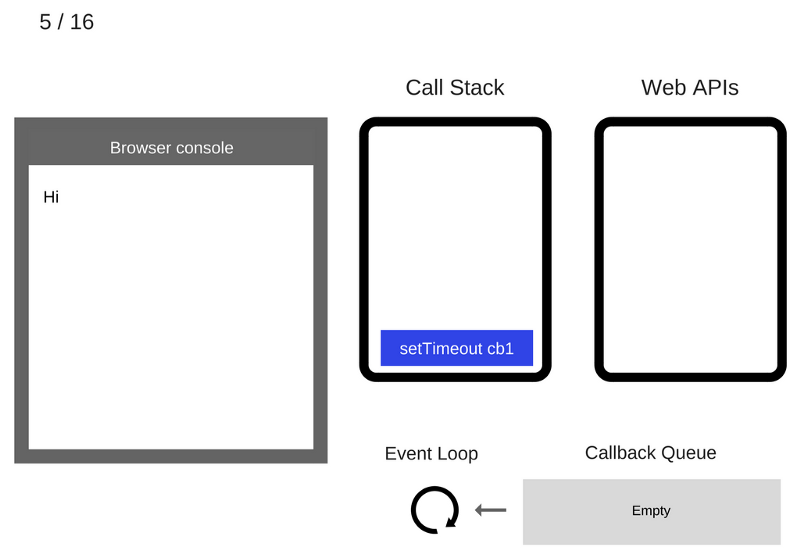
The setTimeout (function cb1 () {...}) command is executed. The browser creates a timer that is part of the Web API. He will do the countdown
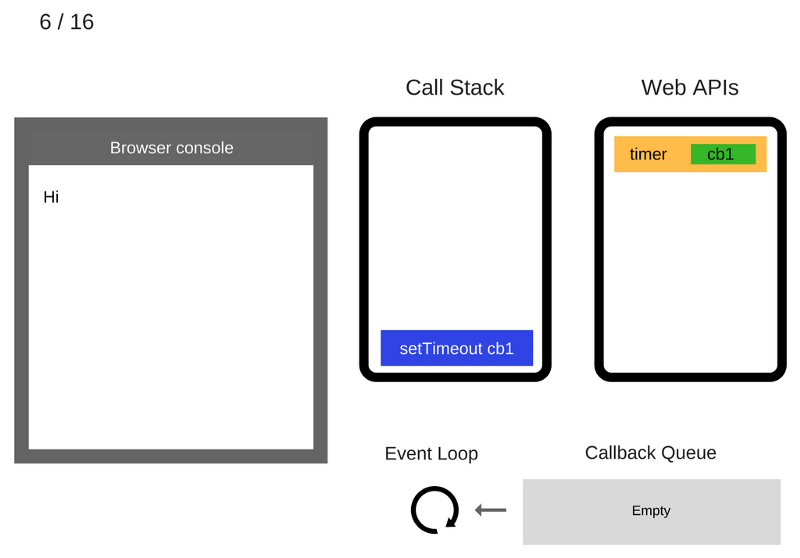
The setTimeout (function cb1 () {...}) command has completed and is removed from the Call Stack
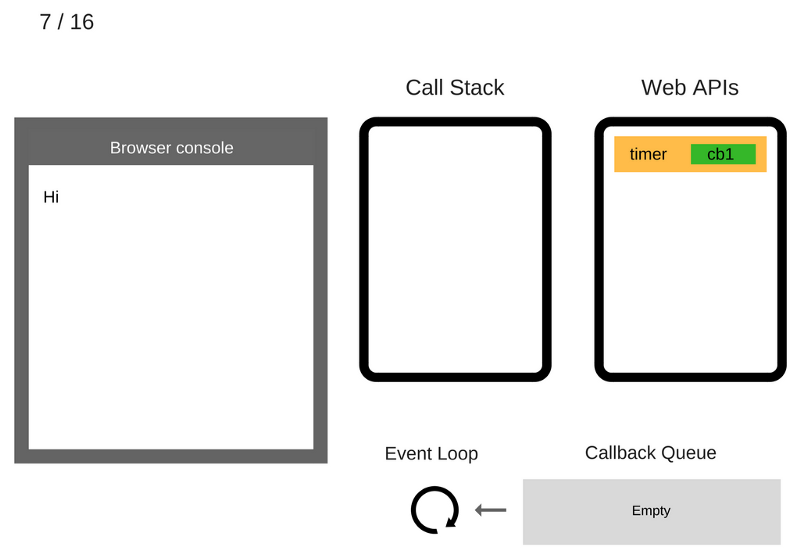
The console.log('Bye') command is added to the Call Stack
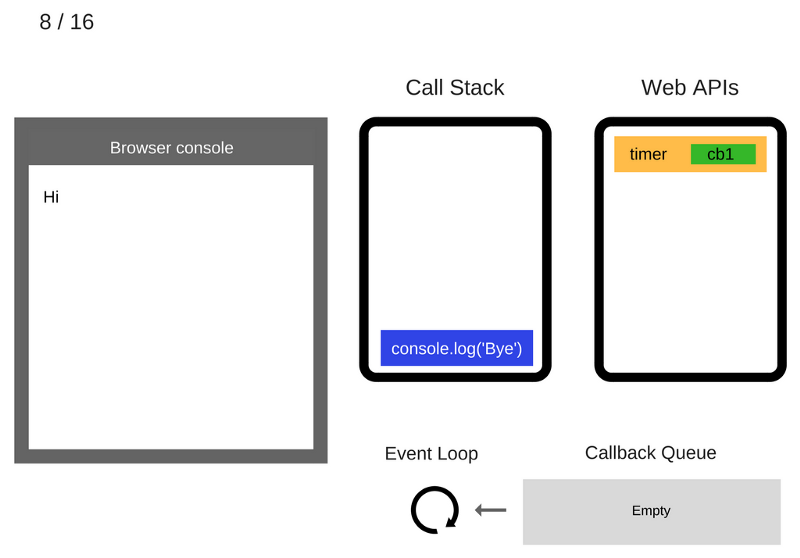
The console.log('Bye') command is executed
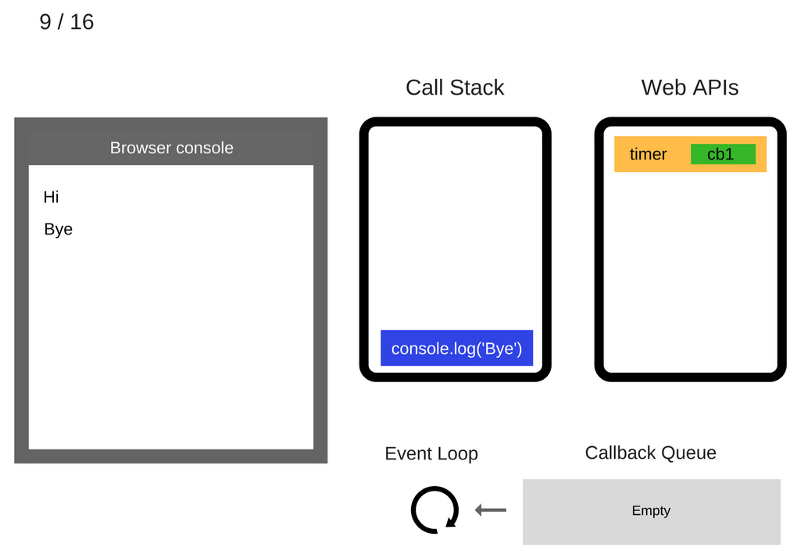
The console.log('Bye') command is removed from the Call Stack
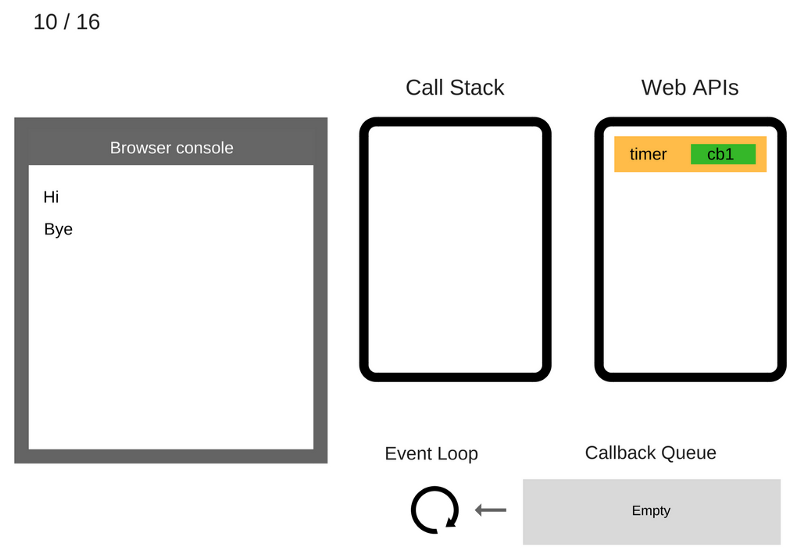
After at least 5000 ms have passed, the timer exits and puts the cb1 callback in the Callback Queue
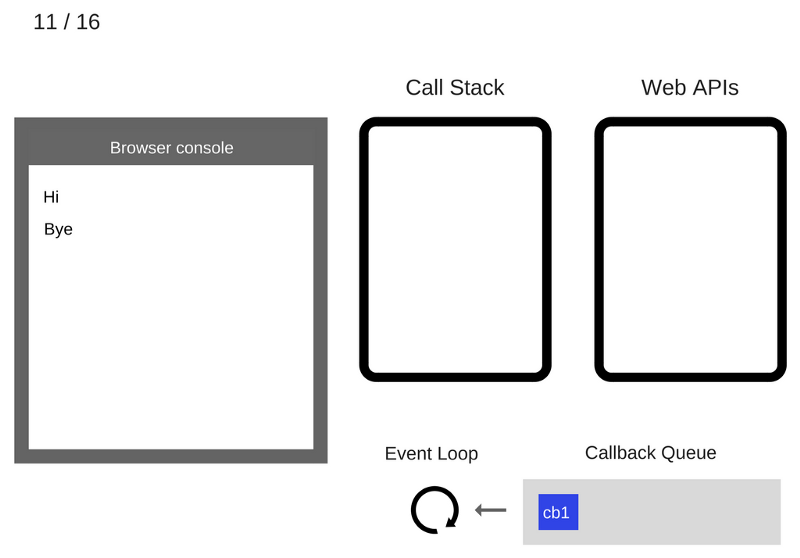
The Event Loop takes c the cb1 function from the Callback Queue and places it on the Call Stack
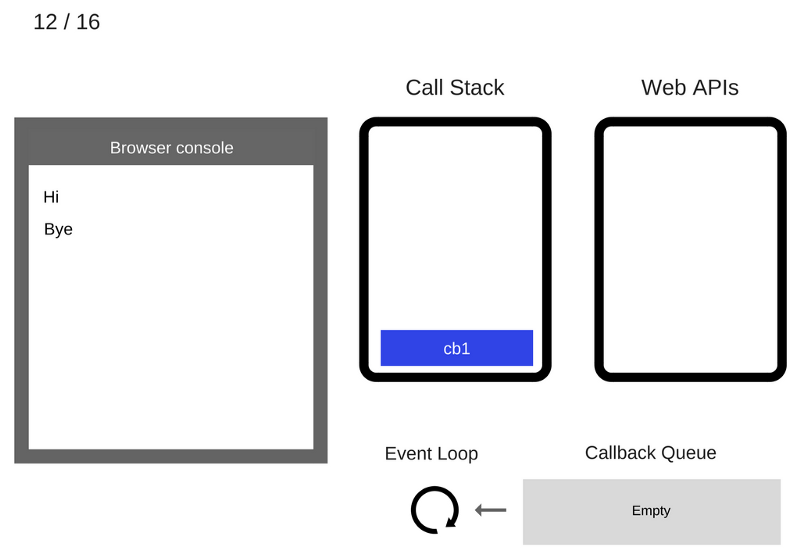
The cb1 function is executed and adds console.log('cb1') to the Call Stack
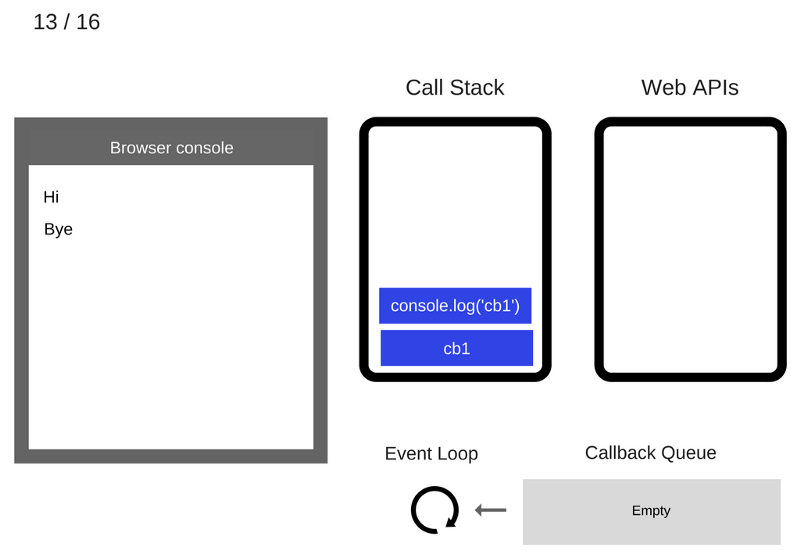
The console.log('cb1') command is executed
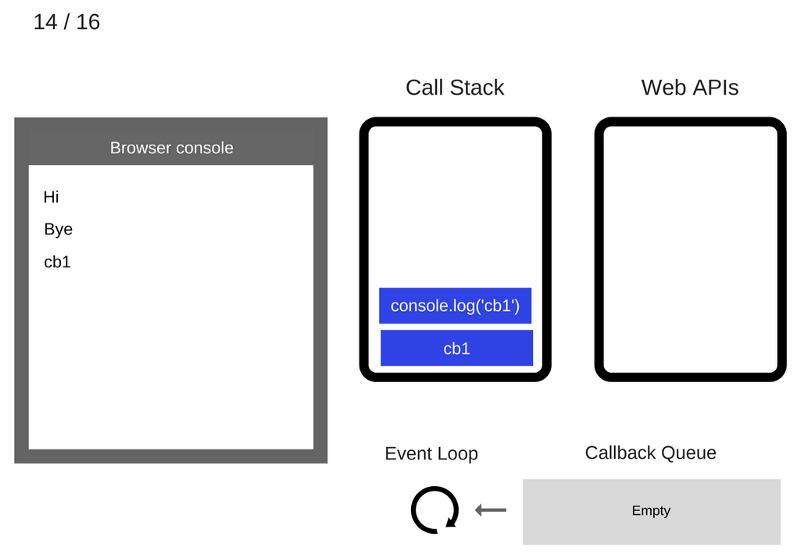
The console.log('cb1') command is removed from the Call Stack
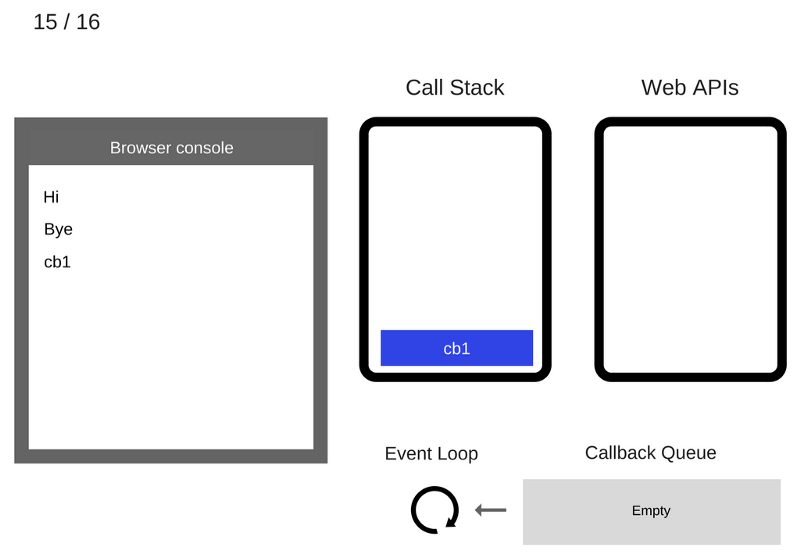
Cb1 function is removed from the Call Stack
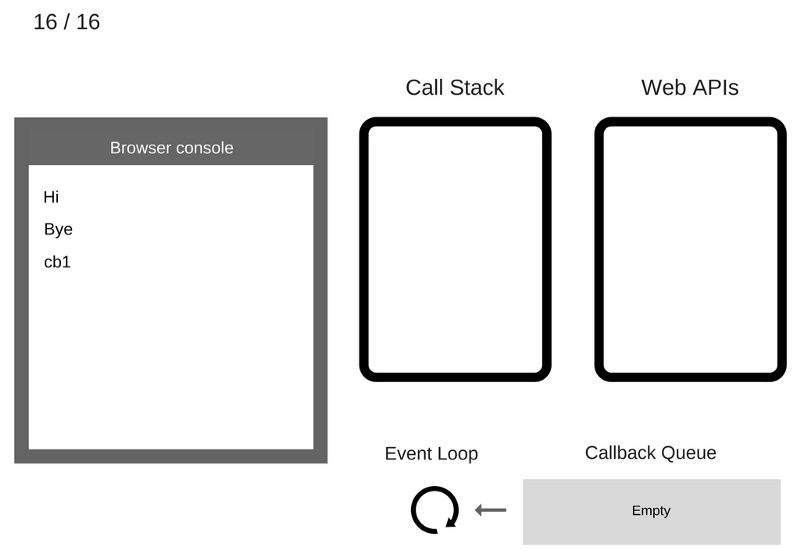
For consolidate knowledge - animated form of Event Loop